380 Vdc - opening up the route to expansion
What do you do when the amount of data you are processing is skyrocketing, and further expansion of server capacity is blocked due to power supply constraints? This is the story of how a service provider in exactly that situation found the key which opened the route to increased capacity.
Ever more data
The increasing demand for bandwidth keeps pushing the development of telecom and computer equipment. However, the more advanced equipment – the more power you need to support it.
A few short years ago, planners could assume a power level of 750W to 1,250W per rack for the deployment of state-of-the-art servers. Today’s planners project power levels as high as 15kW or more for the ICT equipment that will be delivered in the coming years.
This is a challenge. Most telecom service providers’ networks are dominated by traditional 48 Vdc power plants that feed the 48 Vdc telecom equipment. Many of the plants are already operating near capacity. Upgrading, replacing or supplementing the existing plants with new 48 Vdc power equipment is, however, not a viable solution.
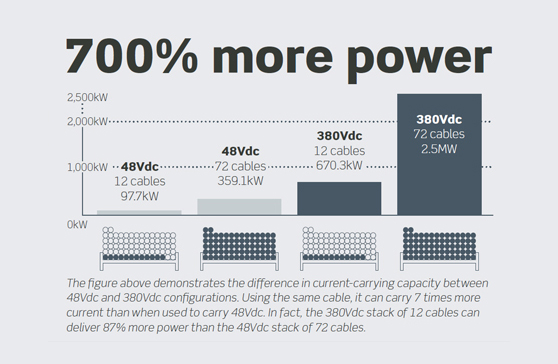
Cable congestion creates bottlenecks
Robert Ambriz, one of Eltek’s network architecture specialist, explains:
– The most significant capacity issue is the extensive cable congestion that restricts power delivery into the ICT areas from the 48 Vdc systems. These extremely large stacks of cables are the result of the high current levels associated with 48 Vdc powering, the requirement to support worst-case load projections and the need to adhere to tight voltage drop considerations, says Robert.

During his 25 years in the telecom industry, Robert has focused on improving infrastructure efficiency and reliability. He has held technical positions in repair, supervisory, management and engineering. Robert has been identified as one of the early adopters of 380 Vdc technology.
Going from 48 Vdc to 380 Vdc
One of Eltek’s customers, a North American service provider, has taken the step from 48 Vdc to 380 Vdc power transfer, assisted by Robert and his expert colleagues from Eltek.
– The company in question had a powering architecture with 48 Vdc rectifier plant and batteries in a power room. The 48 Vdc power was distributed to the loads through battery distributing circuit breaker boards (BDCBBs), located in the ICT equipment area. - It was the large cable bundles between the rectifier system and the BDCBBs that created the congestion, Robert explains.
The customer was preparing for the higher voltage DC future, and had decided to install 380 Vdc rectifiers and batteries at the plant. However, since the existing loads and most of the new loads will operate from 48 Vdc for some time, phase 1 of the strategy was to install a high-efficiency 380 Vdc/48 Vdc converter system in the ICT equipment area.
Since the plan was to reuse the power transfer cables, it was beneficial to install the 380 Vdc rectifier bays near the 48 Vdc plant. However, the batteries can be located wherever there is space, which can even be in outdoor containers.
Extensive tests were carried out to ensure that the rectifier and converter systems were designed and tested to UL standards and other regulatory requirements. There is no doubt that this is a safe solution
Robert Ambriz, Business Development Director, Eltek
The 380 Vdc / 48 Vdc converters support any new 48 Vdc loads being added at the facility, as well as provide relief for heavily loaded 48 Vdc plants. The setup is ready - the 380 Vdc plants will grow over time and the 48 Vdc plants will be eliminated as they reach end of life.
Safe and sound solution
The technical assessment of the system included lab testing which established that a 380 Vdc system is safe, both in terms of personnel safety and reliability. – Extensive tests were carried out to ensure that the rectifier and converter systems were designed and tested to UL standards and other regulatory requirements. There is no doubt that this is a safe solution, – says Robert.
A smart investment
Looking at the comparison table to the left you can clearly see the financial attractiveness of a 380 Vdc vs. a 48 Vdc solution.
– Due to the space limitations the customer was experiencing, a 48 Vdc system was not a realistic alternative in this case.
However, for better understanding they carried out an analyzes of the new 380 Vdc configuration vs. what would have been a comparable 48 Vdc system.
This comparison showed that power cabling was by far the major cost factor, and although the cost of equipment and installation was somewhat higher for the 380 Vdc system, the total saving was as high as 27%. The magnitude of this cost saving served as an additional impetus for our customer to move ahead with its transition to 380 Vdc powering.
Aside from its value in sites that are constrained by cable congestion, 380 Vdc is also a fundamentally more economical alternative to the traditional 48 Vdc approach.
– With a 380 Vdc solution you get an instant relief from the capacity bottleneck and reduced cost. But even more important: you get a sturdy and future-proof solution that has the flexibility to cater for continued explosive growth in data traffic and corresponding power requirements, concludes Robert.




